Research Findings on Career Success
IQ is important, but Emotional Intelligence, including Social Skills (SQ), is even more so.
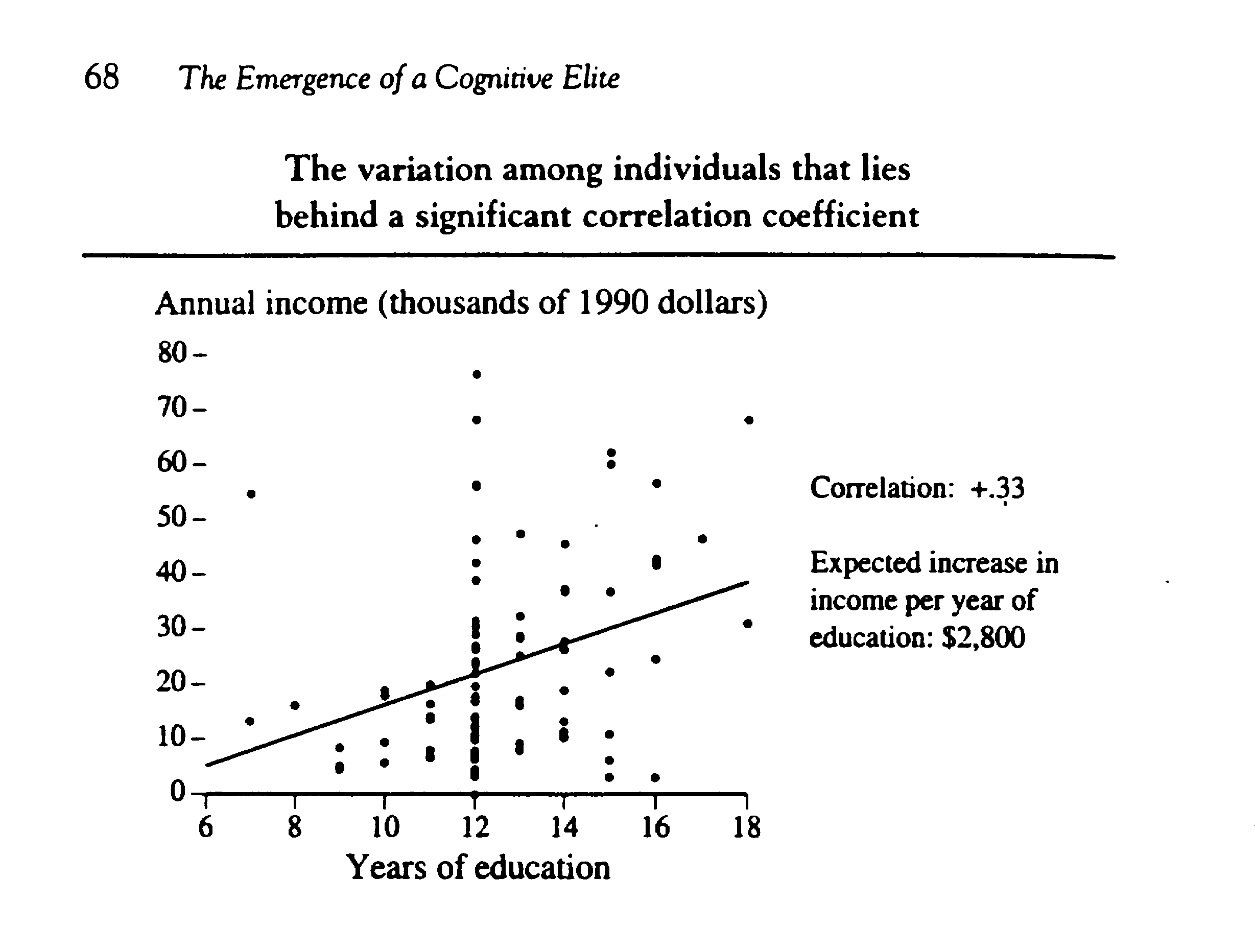
The chart at right is from The Bell Curve by Herrnstein and Murray. It shows a
correlation of 0.33 between a person's annual income and his years of education, which is related to his IQ. .The spread of dots shows that other factors are more important for income. See Gardner's comments on intelligence and The Bell Curve.In his Working with Emotional Intelligence
Goleman wrote: "I found that 67 percent - two out of three - of the abilities deemed essential for effective performance were emotional competencies. Compared to IQ and expertise, emotional competence mattered twice as much. This held true across all categories of jobs, and in all kinds of organizations." Going beyond 67%, Yale professor Sternberg writes in American Psychologist in Nov. 1995: "Between 75% and 96% of the variance in real world criteria such as job performance cannot be accounted for by individual differences in intelligence test scores."The Role of IQ in Career Success
Consistent with the above chart is
Lynn and Vanhanen's 2002 book: IQ and the Wealth of Nations. In it they review the scientific literature and conclude that IQ is an important determinant of educational attainment, earnings, economic success, etc. They find in the United States and Britain that the correlation between IQ and earnings for individuals is approximately 0.35. (very close to the 0.33 in the above chart).IQ seems to account for up to 1/3 of an individual's financial success. But there is little that one can do to improve it; IQ seems to be fixed by around age 5. See
IQ Basics for an expert's explanation the fixed nature of IQ and its other important characteristics. In admissions, Ivy League colleges look for future leaders - for social skills and ambition, in addition to brains.Stanford professor
Steele finds that the SAT is "in a sense an IQ test" and that "the SAT in fact measures only about 18% (ranging from 7% to 30%) of the factors that determine a person's freshman grades." Corroborating this 18% figure, James Maas found that SAT's accounted for 16% of future academic success at his Cornell. The point of all these numbers is that a large percentage of success is NOT related to IQ. Nevertheless, an increasing number of employers are asking job applicants to provide SAT scores. This is a wise trend in hiring, given that up to 1/3 of success in entry jobs is related to IQ. SAT's now largely test.for IQ, but the new SAT's may correlate more with high school grades than with IQ.The other 2/3 of Career Success
Research published in 2006 found that
social skills in youth leads to mid-life success. Social skill was determined by having students circle the names of those they would like to have as best friends and sit next to in class. This is virtually that same method as in this sites's Social Quotient surveys.2002 research
compares high school qualities to earnings at ages 35 and 53. It shows that the effects of IQ are lower than previously thought. Aspirations, socialization, and role models were found to be quite important. Reorganizing a school to promote future success of students would place greater emphasis on non-IQ skills. Some medical schools are now using SQ type surveys as part of their instructional program.Although
IQ is quite similar in men and women, they bring different skills to non-IQ parts of career success. Goleman and Sloan have found that women tend to gel along better with others, while men have greater ambitionGo to:
Go to: Career Success differences of Men and Women
Go to:
How Social Skills and Ambition can get you that jobGo to:
"Energetic" should be added to IQ, social skills, and ambition as a success talentComments to:
VanSloan@yahoo.comRead the
ongoing dialog between Sloan and viewers of this websiteThe ads below are placed by Google.com - they are not necessarily endorsed by this site